Why are blogs important?
Blogging is somewhat of a necessary evil. It can be hard to maintain a consistent quality blog and keep content fresh, but quality content helps build Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for your website. Posting consistent quality content improves your website’s SEO, and that increases your chances of appearing as a search result when a person searches for something related to the content you’ve created. For example, if a person searches for car insurance and you’ve blogged about car insurance a lot, your site may appear in their results. The better your SEO is the higher you’ll rank on the search result page, which increases your chances of the user clicking on your website…and that’s what it’s all about.
How to optimize your blog for search engines?
Optimizing a blog article for search engines, aka SEO, isn’t as complicated as it sounds. In short, all you’re doing is making it so search engine page crawlers and bots can understand what you’re writing about so they can show it to people who are searching for this type of content.
Outside of the content itself being unique and useful, there are several markers that Google looks for when it calculates the quality of your content. Since this content is viewed and scored by bots, some of these markers are format related. This formatting helps the bots understand what the content is, how it’s relative to other content, what aspects are important and so on.
- Unique Content
- Content Formatting
- Featured Images & Alt Tags
- Outbound Links
- Backlinks
- Internal Links
- Meta Data
- Keywords
Unique Content
When creating a blog, it’s best not to search around the web and simply copy and paste from other sources. Not only does it not help your site, it can actually hurt your own domain authority. Search Engine bots will recognize matching content and will know which site had that content first in its database. Not only that, but if the site you copied from has a higher domain authority than your site, the search engine will likely list them in the search result over yours. It would then likely exclude your site because the content matches another result already listed.
Therefore, it’s essential that your content be unique. Of course sourcing material and ideas is fine, but it needs to be rewritten into your own words.
In terms of length, it’s believed google prefers more content to less. Gone are the days of 300-500 words. Now, quality blog content is expected to be 1200-2500 words in length. With that being said, it can be difficult to continuously generate longer blog articles, and something is better than nothing when it comes to posting consistently, so mixing in shorter articles here and there with longer ones won’t hurt your site as long as the article is unique.
Content Formatting
When a bot views your post, it looks for certain formatting to tell the difference between text within the post. Without this formatting,, all of the text will look the same, so it wouldn’t be able to tell the difference between a header or a paragraph. In the same way you used headers and titles when writing an article or syllabus in school, you’ll apply similar formatting in your post.
Headers follow a hierarchy of H1-H6, with H1 being the largest and most important and H6 being the smallest, least important, and/or most “detailed” header.. There can only be one H1 header on a page or post. When you enter the Post or Page name, that will automatically be given an H1 heading tag. From there, descending headers will start with H2 and so on based on their level of importance. See example below.
Post Title – H1
Paragraph Header – H2
Subheader – H3
Detailed-Subheader – H4
Detailed-Subheader – H5
Detailed-Subheader – H6
In the image above, you can see several headers underlined. The H1 header is underlined in red and is the title of the article. The blue underlined is the H2 header and near the bottom where it’s highlighted gray, that’s actually an H3 header.
To change a header, simply highlight it like the image above and click the current header setting to adjust it to a different one.
Even though you may be able to achieve the appearance of a header simply by bolding or enlarging the text, it doesn’t actually wrap it in a header tag (html code that tells the bot it’s a header), which is what’s important. You’ll need to add a Heading Field from the available widgets. Once you have a Heading field you’ll be able to select the header size. Again, the H1 heading has already been applied to the post name, and the page can only have one H1, so you’ll only ever select from H2 or lower.
Simple paragraph text, should never have a header tag selected for it. Always use “paragraph text”. This should automatically be applied when you use the text widget or start typing into a text block on the post or page.
- Featured Images & Alt Tags
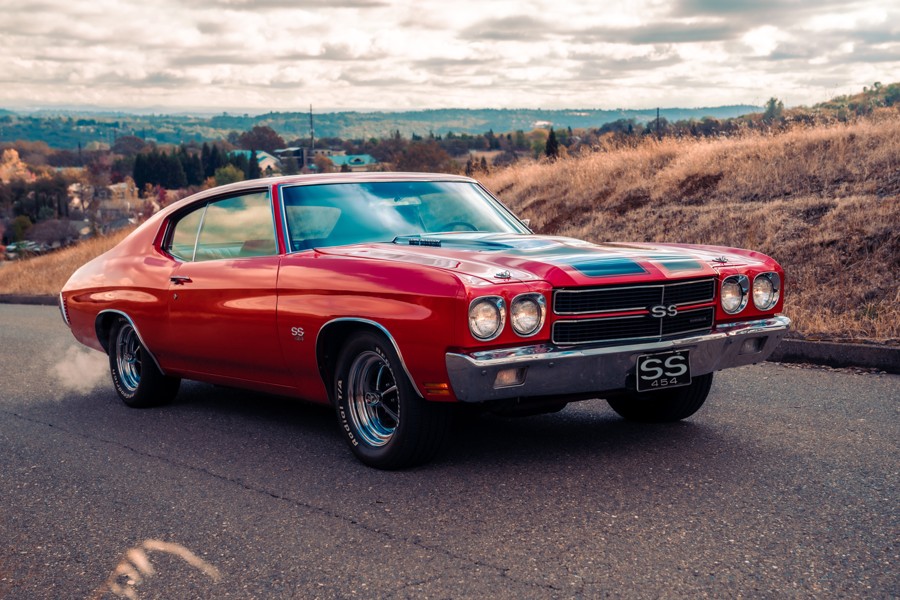
Each post or page should have a “Featured Image”. Ideally, the image should be relevant to the content of the post. If it’s a post about classic car insurance, you would likely want an image of a classic car in it, like the one above.
When uploading a new media file to the site, you’ll see several text fields (Alternative Text, Title, Caption and Description) to the right of the image. Just like the image above. These fields provide the bots with information about this image and how it’s related to the content in the post.
- Outbound Links
Before we get into their importance, let’s discuss what Outbound links are. Links from your website to another website are Outbound links. These links are essentially links to other resources that you used when creating that blog article or to other websites with similar content that you think the reader would like.
For example, let’s say in your article about insuring teen drivers you reference a statistic from IIHS that fatal accidents for 16-19 year old drivers are nearly 3 times more likely than drivers over the age of 20. You would write it something like this:
“According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety fatal accidents for 16-19 year old drivers are nearly 3 times more likely than drivers over the age of 20. ”
Providing Outbound links to higher domain authority sites helps your site by showing that the content you’re providing is similar to this content others already find useful. It’s also good to show recognition to these other sites because eventually you’ll want others to do the same and reference content on your site (backlinks).
- Backlinks
Backlinks are the exact opposite of Outbound links. This is when another website links to your website. This is something that can naturally happen over time as you get more and more content out there. There are also a lot of companies out there that you can pay to post links to your website on sites all over the internet. Be careful though, as you don’t want your site linked to just any site, so make sure you’re being linked on other quality websites. If they’re spammy sites, this can actually hurt your own domain authority and SEO.
- Internal Links
Internal links are when you reference other pages on your own site. This helps keep readers on your website longer. Over time, you want your site to be a giant web of links to other pages and posts throughout your site.
If you write a post about protecting your home from frozen pipes in the winter, you would obviously want to include some links to other articles related to protecting your home and of course your homeowners insurance pages. The same goes for every post you add to the site. It should always have multiple links to other pages on the site.
Here’s how you add a link to text on a post/page. Highlight the text and click the paperclip icon. That paperclip is the universal emblem for a hyperlink (link).
Once you click the paperclip, a new box will appear to enter the url for the link. Simply enter it and hit enter or the curved arrow on the right in the box.
- Meta Tags
Meta Tags are invisible tags that provide data about your page or post. In short, they make it easier for search engines and users to determine what your content is about. Metas are made up of two parts, the Meta Title and the Meta Description.
Meta Title
Meta Description
The Meta Description is the first preview a person will see when your page appears in search results. It’s important to make sure this is precise and accurate of the content provided on your page/post.
Search Engine Preview
As you can see in the Search Engine Preview above, the Meta Title and description are used to create what appears when your page/post shows up in a search result. Best practice is to use the page/post title and site title for the Meta Title (if they’ll all fit). For the Meta Description, you can use a portion of the initial paragraph on the page, or you can write a custom one that is a short summary of the content.
- Keywords
Keywords are ideas or topics that your content is about. If you were to sum up your entire blog article into a few words or less, that would be a keyword. They are also the words someone would use to search for something on a search engine. If I wanted to search for classic car insurance, I would enter “classic car insurance” into google. Google would use my search query to locate pages with content related to those keywords, so in a sense you’re telling google, when someone searches for this, show my blog/page, but there’s a catch…
Your content has to match your keywords and your keywords need to be embedded throughout your content. This is why we use an SEO tool like the one in the image above on each page and post to verify that your content meets many of the SEO parameters I’ve mentioned in this article. It will scan the page and tell you if you don’t have your keyword in a header tag or if you’re missing your meta tags and so forth. You don’t have to get the analysis to be completely green, but you should make sure to get as close to green as possible with all of the suggestions, and make sure there are no “Red” suggestions.